Section 2 Methods for Instructional Design
 I.Thinking
I.Thinking
【Case Reflection】
Instructional design has become a hot subject and is often chosen as a topic for reports and contests. However, Mr Y, who has been working as a teacher for 30 years, is an exception to this increased awareness. In his view, instructional design is just preparation for class and design of teaching plans. As we know, instructional design is a branch of teaching pedagogy.
In China, instructional design is a research field of educational technology which itself is a sub-branch of education.
In your opinion, what makes instructional design an academic field? What are the essential differences between instructional design, preparation for class and design of teaching plans?
 II.Instructional Design Models
II.Instructional Design Models
Due to the tremendous differences in the scope of various instructional systems and task levels in design practice, compounded by the different working environments and professional backgrounds of designers, there are different focuses in various instructional designs. Therefore, different instructional systems, conditions and philosophies require their own design models. Precisely because of this, there have been hundreds of instructional design models since the 1960s when exploration in this field began. However, considering current English instructional concepts as well as instructional conditions and facilities in China, instructional design should adopt the constructivist model.
Piaget's theory of cognitive development, Vygotsky's zone of proximal development and Bruner's cognitive structuralism together contributed to the establishment of constructivism. According to constructivists, learning is a process where learners take the initiative to construct psychological representations. It includes structural knowledge and nonstructural background experience with emphasis on the significance of student voluntary construction of knowledge, that is to say, students construct new knowledge based on previous personal experience, psychological framework and convictions.
Within the framework of constructivist learning theory, instructional design should follow the pattern as shown in the figure below.
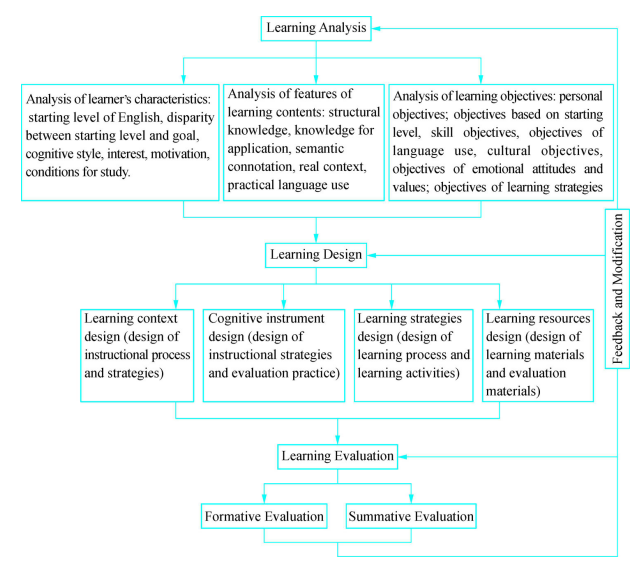
Figure 6-2 Instructional design model based on constructivist learning theory
 III.Instructional Design Forms
III.Instructional Design Forms
Outcomes of instructional design can be presented in two forms: table and flowchart.
Tabular design refers to presenting the content of instructional design in the form of tables, based on the concept of instructional design. It shares many similarities with regular teaching plans except that activities led by teachers and progress made by students should be designed separately and the objectives of each part should be clearly identified so that instructional processes can really meet the needs of students. This design is suitable for experienced teachers.
In flowchart design the instructional methods and media equipment are represented in different symbols so that teachers can be easily aware of these factors. It is suitable for less-experienced teachers.
can be easily aware of these factors. It is suitable for less-experienced teachers.
Below are two examples of instructional design forms:
1.Table form of instructional design
This is an instructional design case sourced from a senior middle school English teaching experiment conducted by Kwesting Lu of Central China Normal University. It takes the form of a table.
Analysis of teaching material
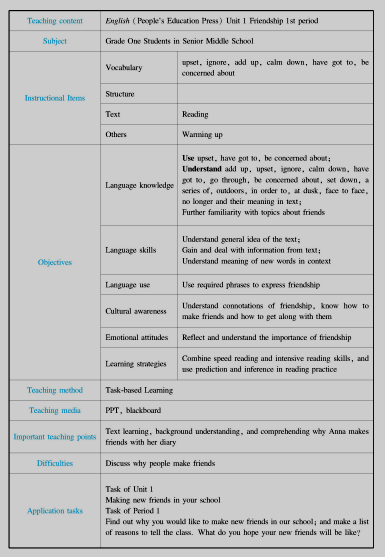
Process of classroom instruction (extract)
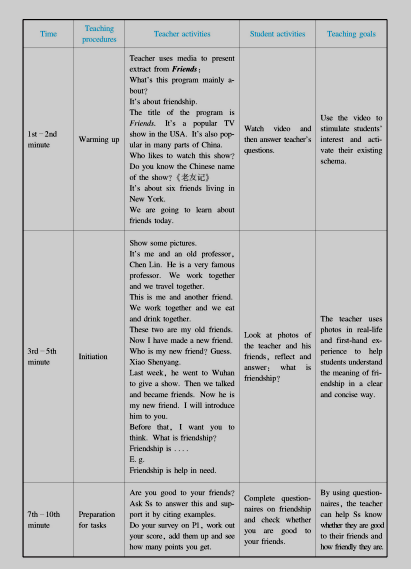
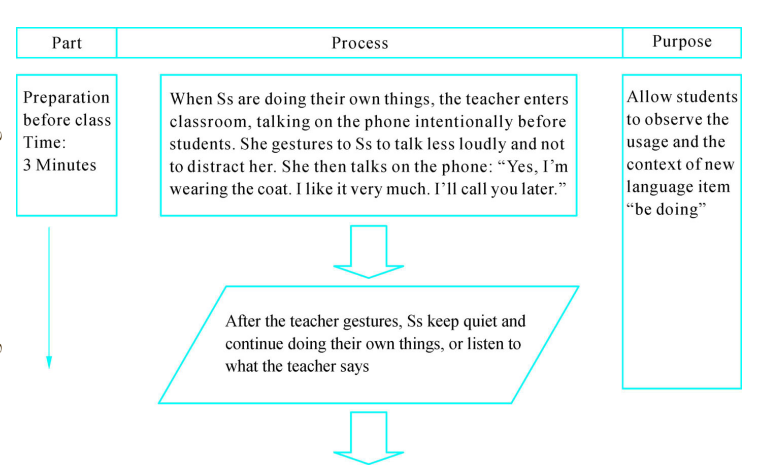
2.Flowchart form of instructional design
Instructional design can also take the form of flowcharts. This is more suitable for emphasizing the use of media in classes with different signs representing different uses of media.
Analysis of instructional content (omitted)
Flowchart form of classroom instructional process
Flowchart symbols
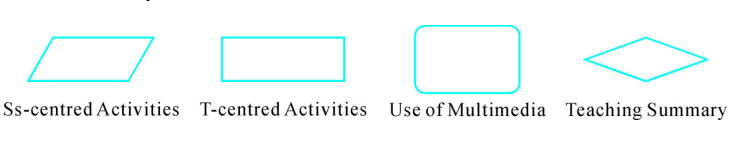
Tables and flowcharts are just alternative ways to represent processes, as illustrated in the case above.
 IV.【Practical Analysis】
IV.【Practical Analysis】
The following is a learner analysis done by a senior middle school teacher. Analyse its shortcomings and strengths.
Learner Analysis (Hubei XX Middle School)
The needs analysis of learners is the basis of instructional design for English language classes. Chomsky stated that language is an innate human ability, which suggests language instruction should focus on students, since only when students' motivation and initiative are fully activated, can the outcome of instruction become effective. Therefore, the instructional design of Unit 7 Living with disease should take learners' needs into account.
The topic of this unit, “illness”, is closely related to daily life and is a very interesting topic for students. As a lead-in activity, an “AIDS Knowledge Test” is given to students in the form of 8 multiple-choice questions to see whether students already have some general knowledge about this disease. Some students may be unfamiliar with this topic, knowing only that it is one of the most challenging medical problems. Therefore, teachers need to adopt various methods, for example, giving students a chance to present their knowledge of the topic if they are familiar with it, or presenting students with relevant pictures and giving them some basic knowledge, e.g. what AIDS is and its means of transmission.
The listening task is to listen to an expert from the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, talking about how they collect the pathogens, analyse patient cases, give suggestions on prevention, and so on. However, students may be unfamiliar with the content, so they need to look through the instructional material before the listening task and then extract specific pieces of information from the material. Students may find the preparation before the listening task difficult. To solve this problem, teachers can design and raise questions before the listening task to help students understand the relevant background information and prompt them to think. After this they return to the material and guide the students to grasp the key words in the listening process and then improve their listening ability effectively.
The speaking task is to discuss what is the most serious cause of ill health, e.g. AIDS, taking drugs, smoking, excessive drinking, etc. In this task, students are divided into groups and each student is asked to share his or her opinions on what is the most serious problem and give reasons to convince other group members. It is a good opportunity for students to use English to communicate authentically, and students should have good support for their own opinions. However, they might come across difficulties in expressing themselves or producing logical reasoning and language organization. If this is the case, teachers could first preselect some relevant but minor topics for students to discuss, thereby preparing them for the later presentation. During the preparation, teachers should give as much help to students as possible, to encourage more students to participate and thus improve their expression and communication abilities.
 V.Chapter Summary
V.Chapter Summary
Instructional design is a modern educational technology based on current learning theories as well as a process in which teachers analyse and design instructional objectives, processes, strategies, and techniques based on learner characteristics. They also collect and evaluate feedback to prepare for instruction. During the process, various technologies and tools can be used to analyse classroom instructional activities in terms of quality and process. Instructional design is usually composed of the analysis of learning needs, learning content and learners; design of instructional strategies, instructional processes and techniques; identification of evaluation objectives and selection of evaluation methods; and design of formative and summative evaluation. It can be divided into four parts: analysis, design, evaluation and feedback with each part having its own features.
Based on current educational concepts and English teaching conditions in China, instructional design is underpinned by constructivism. Therefore, instructional design should start with student learning and its content should vary correspondingly, from instructional processes, strategies, and technology to the design of learning context and strategies. Instructional design can be represented in two specific forms: table and flowchart.
