Section 1 Criteria of Evaluation on Teaching English
 I.Thinking
I.Thinking
【Case Reflection】
Read the following teaching evaluation form(See Table 16-1)
Table 16-1
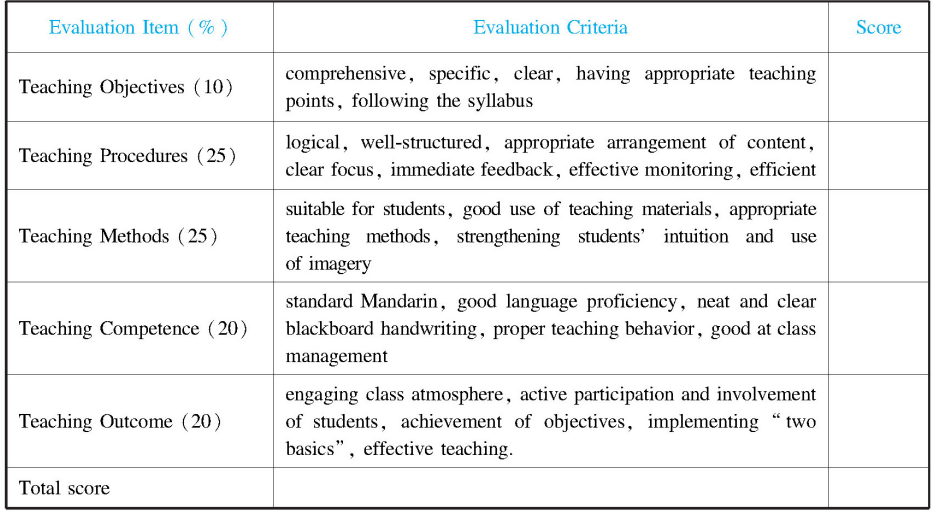
(Source: Department Of Basic Education,Department of Teacher Education. Common Senior Middle School Curriculum Handbook: the Implementation of National Curriculum Standards,2006:105)
Please reflect: What is the focus of this evaluation form? Do you like this kind of evaluation? What may be some of the disadvantages of this form?
 II.Concept of Teaching Evaluation
II.Concept of Teaching Evaluation
The public elementary and middle schools in China are wholly funded by national and local governments, including facility construction, teachers' salary and students' tuition fees. Therefore,it is necessary to conduct the kind of evaluations that we find in the national audit of the fund for important projects. This chapter will introduce ways to do teaching evaluation.
According to N.E. Gronlund,evaluation can be represented by the formula evaluation equals quantitative measurement plus qualitative measurement plus value judgments(Qu & Chen,2003:7). Teaching evaluation is an important part of education evaluation and is based on educational value and evaluation criteria. When done with feasible and proper evaluation methods through systematic information collection and analysis,teaching evaluation can assess classroom teaching and learning and their outcomes.(Zheng,2004:215). “Teaching evaluation is the evaluation of classroom management,learning achievement and other related aspects. It is an analysis of the classroom teaching effect and the factors that affect teaching,which are an indispensable part of teaching. It plays a very important role in improving classroom teaching and teacher development”.(Lu & Wang,2006:262)
 III.Disadvantages of Traditional Teaching Evaluation
III.Disadvantages of Traditional Teaching Evaluation
Traditional teaching evaluations:
●emphasize assessment,and overlook teacher development;
●emphasize administrative management,and overlook teaching improvement;
●emphasize the teaching effect,and overlook learning achievement;and
●emphasize observer evaluation,and overlook teacher self-reflection and student evaluation.
“The purpose of evaluation is practical and is approached from the perspective of the administration and management,which uses the evaluation to appraise teachers. The objectives of evaluation are distorted. Evaluation should focus on assessing the process of teaching,instead of appraising the teachers or otherwise the function of teacher development is lost(Wang et al.,2004:28). The traditional evaluation only focuses on whether teachers have finished the teaching plan. Do our students understand what was taught? Do they know how to learn? Do they like this way of teaching and learning? All these are not taken into consideration. Teachers are only passive listeners to the lesson observers when discussing the class being evaluated.
Students are also excluded from the discussion. Evaluation is completely quantitative. The observer simply gives a score to the lesson without any discussion with the teacher,thus the evaluation is not helpful in improving teaching.
 IV. Teaching Evaluation under the National Curriculum Standards
IV. Teaching Evaluation under the National Curriculum Standards
(I) Basic ideas
Teaching evaluation under the National Curriculum Standards aims “to promote students' and teachers' development,and to use what students learn to evaluate how teachers teach”(Zhou & Zhao,2004:13). Promoting student development has two aspects. Firstly,it is reflected in the teaching objectives. The basic goal of teaching according to the National Curriculum Standards is for students to acquire language knowledge and skills with systematic organization of teaching content. A more important goal is that we should help students form their own development objectives. Secondly,it is reflected in the teaching process. We should study teaching strategies and arouse student enthusiasm for learning. Promoting teacher development means the focus of evaluation is not merely on appraising the effectiveness of teaching,but to diagnose what is wrong with the teaching. As such,the evaluation may help us to pursue our own goals of improvement. Using what students learn to evaluate how teachers teach may be done through evaluating students mood,attention,participation,interaction,thinking and products”(Wang,2004:11).
(II) Development trend
Foreign language education is faced with challenges and changes brought by new concepts and methods of evaluation worldwide. Teaching evaluation evolved from only using quantitative methods to using more qualitative methods,from merely appraising teachers to promoting teachers' development. In 1985,the report of Her Majesty's Inspectors of Schools in England marked a turning point for the use of evaluation. It advocated the separation of evaluation and the system of rewards and penalties. This report enabled evaluation to change from being summative to formative. After the 1980s,influenced by Western education,China's evaluation system also changed. With the implementation of the National Curriculum Standards,teaching evaluation began to change in the following ways: evaluation began to emphasize teaching improvement;evaluation began to use a combination of self-evaluation and peer evaluation so teachers were no longer passive listeners;the focus of evaluation shifted from focusing on teaching to more on learning and emphasized that classroom teaching should promote student development in language knowledge,language skills,learning methods,attitudes and values;evaluation criteria became more flexible,advocating individual styles of teaching;and the method of evaluation moved to incorporate more qualitative methods such as case study,classroom observation and portfolios(Qi,2002,cited in Common Senior Middle School Curriculum Handbook:the Implementation of the National Curriculum Standards).
(III) Theory
Constructivism provides a solid theoretical basis for teaching evaluation under the National Curriculum Standards . “Education is to empower learners to think for themselves;education is best put into practice by presenting issues,concepts and tasks in the form of problems to be explored in dialogue rather than as information to be ingested and reproduced. The motivation to master new problems is most likely to spring from having enjoyed the satisfaction of finding solutions to problems in the past”(Glaserfeld,cited in Williams & Burden,2000:49). Therefore,there are six aspects to consider when evaluating the effectiveness of a class. The first is if students are actively involved in learning. The second is if there is teacher-student and student-student interaction. The third is if the class provides suitable learning materials,time and space to allow students to take initiatives. The fourth is if students really understand what they learn. The fifth is if evaluation attaches importance to student self-reflection and reflection on other students' work. The final aspect is if students have a positive experience and attitude toward the subject.
(IV) Evaluation indicators and principles
The evaluation that is often used in teaching evaluation is the use of scales to evaluate the different aspects of teaching. The evaluation indicators include teaching objectives,teaching content,teaching means and methods,teaching procedures,teaching competence and teaching effect. This system is suitable for a comprehensive evaluation of teaching competence. However,the trend for evaluation is to promote the development of both teachers and students,so we should review the evaluation criteria and make evaluation more relevant to the development goals (Lu & Wang,2006).
In teaching evaluation,we conduct evaluation and are evaluated as well. This demonstrates the features of multiple perspective evaluation. Classroom teaching is dynamic,so evaluation should follow the principles below(Lu & Wang,2006:264):
1.Is the class helpful to the development of both students and teacher? The evaluation should help improve teaching method and teaching design. Did we make any progress in class management? Does it demonstrate our professional development?
2.Did we participate in the process of evaluation? In the past,we were always just the audience,passively listening to the comments of others and waiting for the assessment. This kind of evaluation is only an administrative process to distinguish the “good” teachers from the “bad” ones. Teaching evaluation should involve teachers,including determining evaluation indicators and participating in the whole process.
3.Was the evaluation limited to assessing the teaching outcomes? It should also attach importance to every stage of the entire teaching procedures,from teaching design to teaching practice.
4.Was the evaluation multi-dimensional with a variety of evaluators,evaluation methods,evaluation content and means of analysis? The evaluators can be experts in the field,supervisors,peers,students or teachers. Evaluation methods can include evaluation scales,evaluation dialogue,and evaluation seminars. Evaluation content should include teaching objectives,teaching plans,teaching practice,teaching outcome and input. There should be both quantitative and qualitative analyses(Lu & Wang,2006:265).
5.Was it efficient based on a rate of return,which means calculating the ratio of teaching outcome to the time and effort invested per unit time(Yu,2007)? This is an important criterion to evaluate whether teaching activities are appropriate.
6.Did the evaluation include evaluating the art of teaching? The art of teaching can be seen through the teacher's various skills and teaching competence,including language proficiency,use of body language,and handling of different stages of class(e.g. opening,closing,questioning). In fact,evaluating the art of teaching is also the evaluation of teaching competence and teaching process. When teaching,teacher language should be clear,accurate and to the point. Teachers should be good at managing each stage and able to arouse student interest.
(V) Dimensions and Criteria for Evaluation
There are several dimensions for evaluation under the National Curriculum Standards(Wang et al.,2004). They include the evaluation of how the learners learn;learning achievement;learning outcome;teacher use of roles;the creation of the learning environment;and the application of educational technology. In addressing how learners learn,teachers should enable learners to be actively involved in the learning process,and learn through inquiry and research. Learning through reception is also used but it should follow the “meaningful reception learning theory” put forward by Ausubel. The evaluation of student learning achievement includes: active student involvement;independent thinking;active exploration;free expression;cooperation with others;imagination;willingness to disagree;and interest in learning.
The evaluation of learning outcome includes three aspects. The first is the knowledge objective,which evaluates if learners master what is taught. The second is the objective of capability,which evaluates whether they have learned how to learn. The third is the objective of affective factors,which evaluates if they enjoyed learning.
Teachers' handling of their roles,the creation of learning environment and the application of educational technology form the part of evaluation from the teachers' perspective. Teachers should be responsive in changing roles,serving as the organizer,guide and collaborator. Teachers should create a relaxing,democratic,equal and interactive environment which promotes learner autonomy,communication,and individuality. Teachers should also make use of educational technology in teaching.
The evaluation should take the following aspects of classroom teaching into consideration. Firstly,teachers cannot ignore the foundation of the teaching objectives. Secondly,teachers should ensure the integrity of the whole module. Thirdly,teachers should cater for individual differences. Fourthly,teachers should emphasize students' ability to structure knowledge under their guidance. Fifthly,classroom teaching should be open and active. Finally,teachers should pay attention to fostering students' positive attitudes (Common Senior Middle School Curriculum Handbook: the Implementation of the National Curriculum Standards,2006:105).
Wang(2005:198)cited criteria for teaching evaluation used in the US and England. One of the criteria used in the US has four components: the organization of learning content;creation of learning environment;and development of teaching and teachers. The criteria of evaluation in England(See Table 16-2)includes learning atmosphere;classroom environment;resources;the teacher as planner;the teacher as deliverer or leader;the teacher as facilitator and guide;and the role of students. These two sets of criteria attach importance to the development of both teachers and learners.
Table 16-2 Criteria for the management of effective learning
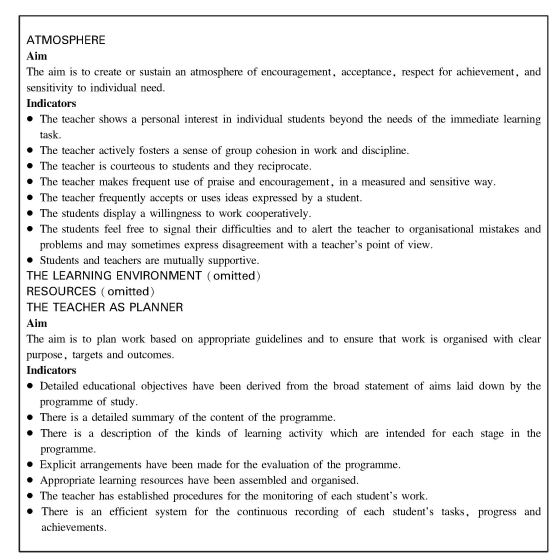
(Source: Cyril & Doreen Poster 1993)
(VI) Evaluation Methods
Evaluation of classroom teaching can be performed by experts in this field,leaders,colleagues,students or teachers themselves. Methods include classroom observation,interviews with students and colleagues,questionnaires and teaching journals.
1.Classroom Observation
Classroom observation is a way for observers or researchers to gather information by personally visiting a class or by using tools such as audio and video recorders,to directly or indirectly observe different aspects of teaching and doing research based on the information collected. Richards and Lockhart(2000:24)stated guidelines for classroom observation. “Observation should have a focus. Observation should use specific procedures. The observer should remain an observer.”
There are two approaches to observing language classrooms: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative techniques include written records of the observer,which always have a focus. The focus can be teacher instructions,questioning strategies,transitions in class,time for student discussion and activity,group work and interaction in class. We can also use audio or video recording of lessons. Then the observers and the teachers can watch or listen to the recording to evaluate and analyse the teaching. Simple forms can help record the information. The following is an example.
Table 16-3 Observation of teacher questioning

Checklists and forms to be filled in or completed are the common tools used in a quantitative approach. The observer records what happened in the class and assigns a grade and evaluates the class.(Richards & Nunan,2000:47).
Sample 1: Classroom management
Rate the lesson according to the following key:
Key:
1.Does not at all reflect what went on
2.Only marginally reflects what went on
3.Neutral
4.Describes rather well what went on
5.Accurately reflects what went on
1.There were no cultural misunderstandings. 1 2 3 4 5
2.The class understood what was asked of them at all times. 1 2 3 4 5
3.All the instructions were clear. 1 2 3 4 5
4.Every student was involved at some point. 1 2 3 4 5
5.All the students were interested in the lesson. 1 2 3 4 5
6.The teacher carried out comprehension checks. 1 2 3 4 5
7.Materials and learning activities were appropriate. 1 2 3 4 5
8.Student groupings and sub-groupings were appropriate. 1 2 3 4 5
9.Class atmosphere was positive. 1 2 3 4 5
10.The pacing of the lesson was appropriate. 1 2 3 4 5
11.There was enough variety in the lesson. 1 2 3 4 5
12.The teacher did not talk too much. 1 2 3 4 5
13.Error correction and feedback were appropriate. 1 2 3 4 5
14.There was genuine communication. 1 2 3 4 5
15.There was skill in organizing group work. 1 2 3 4 5
16.There was opportunity for controlled practice. 1 2 3 4 5
17.Students were enthusiastic. 1 2 3 4 5
18.General classroom management was good. 1 2 3 4 5
(Source:Nunan,D. 1988 cited in Richards & Nunan 2000:79)
Sample 2: The effectiveness of teacher questioning
Table 16-4 Effectiveness of teacher questioning
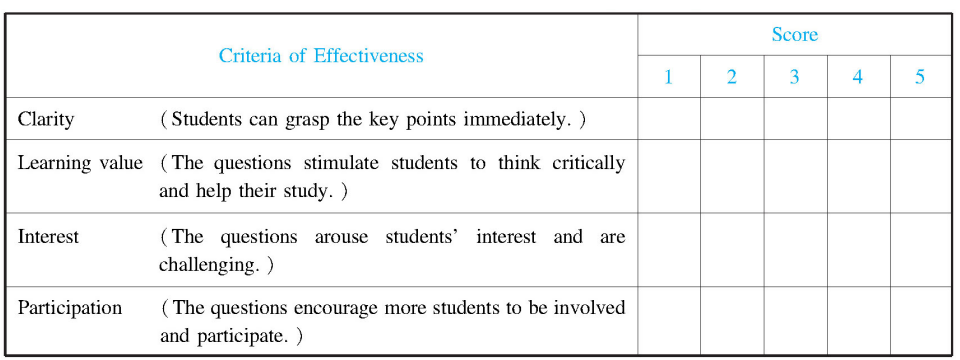
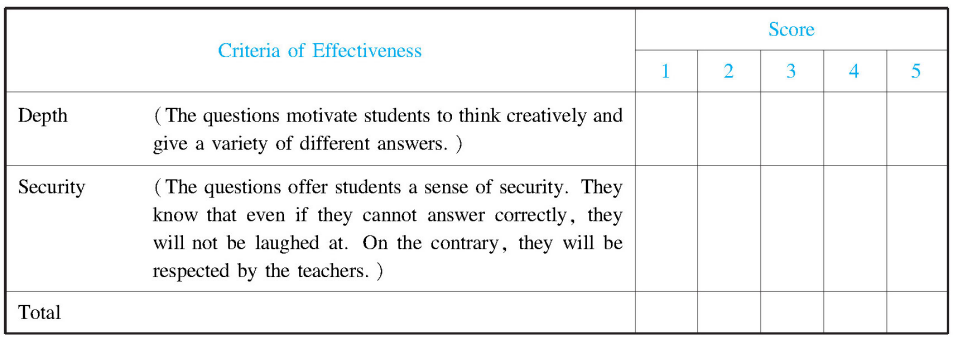
Note: 1,2,3,4,5 represent the score given to each criterion.
Richards & Nunan(2000:47)pointed out the advantages and disadvantages of the qualitative and quantitative approaches. A qualitative approach provides rich,descriptive data about what happened in the classroom. The observer can capture a broad picture of the lesson,instead of focusing on a particular aspect of it. But they are so broad that it takes a highly trained observer to conduct a competent and reliable observation. An untrained observer may be overwhelmed by the complexity of what goes on and not be able to focus on important events as they unfold in the classroom. Quantitative approaches,on the other hand,are relatively simple to construct or revise and to use. The observer who uses these tools does not have to be highly trained in their use and interpretation. Quantitative approaches are more objective and reliable but they cannot capture many aspects of the lesson.
2.Interviews with Teachers and Students
Interviews can be also used to evaluate classroom teaching. They involve eliciting feedback from students and teachers,which cannot be obtained through classroom observation. Questions need to be prepared before the interview and they should be specific. Questions like “Do you think it was a good class? ” should be avoided.
Sample: Interview about group work(the interviewees are students)
1.What was your role in your group in the activity just now? The leader,time-keeper,record keeper? Did you have clear and distinct roles for each person?
2.Did your teacher ask you to play different roles in the group work?
3.Did you like the atmosphere in your group?
4.What did you learn from the group work?
5.Do you have any suggestions on how to improve the implementation of the group work?
3.Questionnaires
Questionnaires are a useful way of gathering information about the affective dimensions of teaching and learning,and include such things as beliefs,attitudes,motivation,and preferences,and enable a teacher to collect a large amount of information relatively quickly(Richards & Lockhart 2000).
