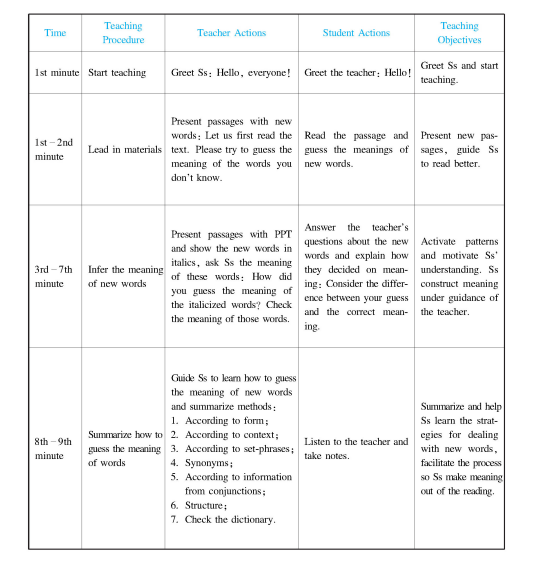
Section 1 Concepts of Instructional Design
 I. Thinking
I. Thinking
【Case Reflection】
An experienced teacher of writing in English, who had been abroad for further study in the United Kingdom, established an elective course in her school to improve student writing skills. A total of 36 junior students were selected to attend the writing course.
The teacher presented students with her English diaries and writing, explained her own experience and what she had learnt through writing, and then asked the students to write by imitating what she had written. Gradually, students became able to write short passages in a style similar to hers. However, a semester later, the teacher was surprised to find only limited improvement in the students' writing skills.
In your opinion, what are the reasons for the limited effect of the teacher's writing course?
 II.Concepts of Instructional Design
II.Concepts of Instructional Design
Design is an activity in which plans are made according to specific principles, methods and techniques to implement improvement. These plans aim to create something new or resolve problems. Instructional design refers to the design of action plans made in accordance with known principles, approaches and techniques, targeted at increasing the effectiveness of the teaching process. Instructional design can also be viewed as a collection of techniques, a process or a set of concepts.
1.Instructional design as techniques
According to the famous American instructional designer, Merrill, instruction is a science, and instructional design is a technology based on this science. Instruction as a science-based technology aims to help students acquire appropriate knowledge and skills; while instructional design is a technology for developing learning experiences and environments which promote students' acquisition of specific knowledge and skills (Yang Jiumin et al., 5) .
As a design technique, instructional design is undertaken to improve teaching effectiveness. In addition, the priority of instructional design is to design efficient instructional activities based on the learning experience and environment.
Instructional design, as a technology, is based on established principles, methods and techniques. To fully grasp this technology requires sound knowledge of these principles, methods and techniques. Instructional design as a technology has its own set of technical tools and mastering these tools is key to implementing the goals set in instructional design.
2.Instructional design as a process
Instructional design can also be seen as a process consisting of a series of divisible activities.
Instructional design has long been defined as a systematic approach to analyzing problems encountered in instruction, finding methods and ways of resolving the problems, evaluating instructional outcomes, and adjusting and identifying new instructional plans. The prominent instructional designer Gagne once pointed out that instruction is a series of events to influence learners by promoting learning, while instructional design is a process of systematically outlining the instructional system. Kemp suggested in 1994 that instructional system design is a planning process in which systematic approaches are used to analyse and research problems and needs from different but interrelated components in the instructional process so as to resolve these problems and then evaluate the instructional outcomes. From the point of view of Smith and Regan, instructional design is a systematic process in which learning and instructional theory are transformed into specific plans for teaching materials, teaching activities, information resources and evaluation (He Kekang, 2005) .
It is generally accepted by instructional designers in China that instructional design is a process. Wu Meina argues that instructional design is a process whereby systematic methods are applied to analyse problems, help devise instructional activities, determine instructional objectives, set up strategies, resolve problems, pilot plans, evaluate the outcomes and finally adjust the plans accordingly. According to He Kekang, instructional design is a process or procedure in which learning and instructional theories inform the instructional objectives, content, methods, strategies and evaluation in order to implement the specific plans and activate instruction and learning. The ultimate purpose of activating this instruction and learning system is to promote learning (He Kekang, 2005) . This point is also made by Pi Liansheng who holds that instructional design is a systematic process that employs modern learning and teaching psychology, communication science, instructional media and other relevant theories and technologies, to analyse problems and needs in the course of instruction, decide and try out solutions, evaluate outcomes, and finally adjust the design according to the evaluation. It is not a journey where effort is made to find objective rules of teaching but rather one in which known rules are utilized to resolve problems faced in the teaching process (Pi Liansheng, 2002) .
The characteristics of the process demonstrate that instructional design is not a closed system but rather an open one which continues as long as the learning process does.
3.Instructional design as concept
Gagne, a famous instructional designer, explicitly stated that our desire to describe all the relevant events (rather than only the events initiated by teachers that have direct influence on learners) can explain why we use “instruction” instead of “teaching” in the expression “instructional design” (Gagne, 1999: 1) . This illustrates that instructional design is not a branch of conventional instructional research but a product of research based on modern learning theory.
In fact, learning theory serves as one of the theoretical bases for instructional design. Instructional design not only underlines the role of teaching in instruction, but also stresses the part played by learning which it regards as even more critical. In this sense, instructional design is the preparation of instructional activities centred on learners. Any of the modern learning theories — behaviorism, cognitivism or constructivism — can be taken as grounds for learner-oriented practice.
We now have a complete picture of instructional design from three different perspectives. By taking all three into consideration and approaching instructional design from the perspective of teaching practice we can say that instructional design is an educational technology based on modern learning theories. It is also a process in which teachers analyse learners' needs and design instructional objectives, process, strategies and techniques in order to prepare for instructional activities. Instructional design techniques and instruments can also be applied to the analysis of class instruction in terms of quality and process as a whole. It is evident that from the perspective of instructional practice, instructional design serves as a technology, a set of tools and a process. It can be employed in preparing for instruction and also in instructional evaluation.
Based on the above analysis, a conclusion can be drawn that since general teaching plans for classes are only preparatory work done by teachers based on their conventional practice (and made without the necessary tools, indispensable process steps and prescribed elements of instructional design), preparation for classes in the general sense does not entail instructional design. Instead, instructional design is a technology with its own system of tools and a process requiring constant modification with instructional concepts targeted at learners.
 III.Instructional Design Process
III.Instructional Design Process
Instructional design generally includes the analysis of learning needs, learning content and learners, design of instructional strategies and techniques, identification of evaluation goals and methods, and formative and summative evaluation design. It usually can be subdivided into the four stages of analysis, design, evaluation and feedback, with each having distinct characteristics. This is shown in the following figure:
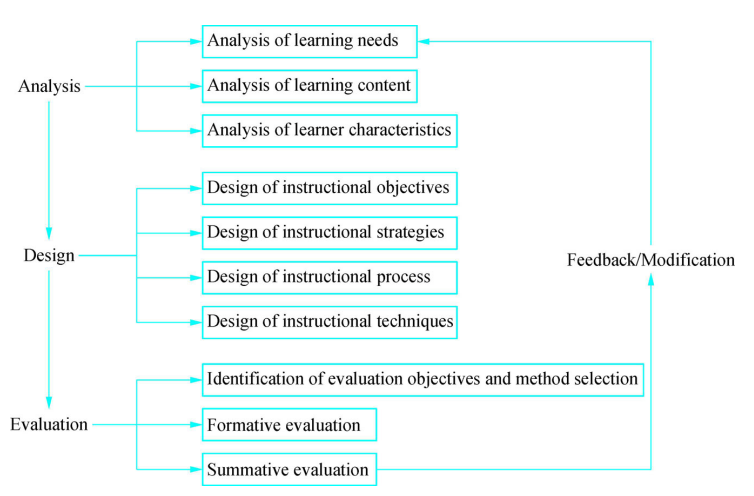
Figure 6-1 General model of instructional design
In spite of the different objectives and factors at various stages, these are all interrelated and integrated as a whole.
Analysis
1.Analysis of learning needs
Learning needs refers to the disparities between learning goals that should be reached through learning activities and the proficiency levels of students. The purpose of analyzing learning needs is to identify those disparities through scientific and systematic surveys.
Identification of learning goals is the key to analysis of learning needs. It requires integration of social needs and personal development needs, consideration of available resources (teachers, students, teaching facilities, teaching media, teaching materials, teaching funds) and different kinds of stimulus and limiting factors in setting balanced and realistic learning objectives.
In the process of identifying learning objectives, long-, medium-, and short-term learning goals should be determined. Equally, goals for a proficiency level, for an academic year, for a semester, for a unit, or for a class should also be considered. In order to identify students' starting proficiency levels, it is necessary to conduct a survey, evaluation and analysis of the academic levels that the students have achieved, especially those factors that directly influence the achievement of learning goals.
It is very important to conduct analysis of learning needs in English instructional design. In addition, we need to set goals for English study in line with the needs of society and the needs for individual development. It is fair to say that many of the difficulties in China's elementary English education are caused by unreasonable learning goals.
In terms of general objectives, the goal of foreign language education is to develop the ability of all learners to use a foreign language. However, it does not follow that all learners will develop into competent foreign language users. Most English learners only aim to succeed in entrance exams to universities and senior middle schools, so they learn only what will be tested. There is also tendency to emphasize grammar and vocabulary in lesson objectives at the expense of cultivating overall language learning abilities.
2.Learner Analysis
Precise analysis of learners is a crucial factor in successful instructional design and it is also the starting point of instructional design. The purpose of this analysis is to provide a basis for the selection and organization of teaching content and learning goals, design of instructional activities, instructional methods, and selection and application of multimedia resources. This is achieved by understanding the psychological profiles, learning styles, and previous knowledge and skills of the learners.
In English instructional design, analysis of learners should include obtaining an accurate understanding of student motivation, personal goals, previous knowledge and skills, cognitive behavior, and psychological influences on learning.
3.Analysis of learning content
Learning content refers to the collection of knowledge, skills, processes, methods, emotional attitudes and values that should be learnt in order to meet learning goals in educational activities. According to the National Curriculum Standards learning content should cover five aspects: language knowledge, language skills, emotional attitudes, cultural awareness and learning strategies. Through analysis of learning content, teachers and students should understand the close relationship between what should be learnt in instructional activities and the instructional objectives.
When teaching a text, teachers find it difficult to convey to students the context of language usage which means that learning goals are not fully met. Serious impact on learning can be caused by teacher focus on semantics on the one hand and ignoring language usage on the other. Teachers need to be deeply aware of the significance of materials on multiple levels, including the semantic meaning, context, and language usage. Only in this way can students fully develop comprehensive language skills.
Design
1.Design of Instructional Strategies
Instructional strategies entail general design of the procedures, methods, forms, media and other elements for instructional activities, to fulfill instructional tasks and attain preset objectives. Instructional strategies include sequential design of instructional content of knowledge and skills, systematic instructional tasks in expectation of student reactions, and design of organization models of instructional activities in addition to ways to present information in various media. It can be further subdivided into division of classes, design of instructional sequence, and design of specific instructional activities as well as selection and design of organization models.
The design of instructional strategies must be based on instructional objectives, consistent with instructional content, and suited to the characteristics of the learners. In addition, feasibility of the strategies should be taken into account. Designs should be creative, and activities should be flexible. All parts of the design should be organized to form a systematic and comprehensive whole.
Instructional strategies
can be classified according to different criteria and the generally accepted classification is: (1)
organizational strategies
for organizing a general instructional process, arranging detailed instructional procedures and presenting specific instructional content,(2)
transmission strategies
for determining transmission forms, selecting transmission media and arranging the order of the information transmission; (3)
management strategies
for coordinating the organizational strategies and transmission strategies. All of these strategies are indispensable in instructional design for English teaching in schools.
2.Design of Instructional Processes for English Language Teaching
Task-based Learning (TBL) is the instructional process advocated in the National Curriculum Standards. The following elements should be covered in instructional design for TBL:
(1) Presentation of tasks
It is important to inform students what the tasks are that they need to complete and to give them a complete and clear idea of the learning objectives.
(2) Preparations for tasks
This part of the language learning process is divided into two main steps, namely exposure and intake. Language exposure, also called language input, is a process during which teachers expose students to the language to be learnt. Intake occurs when students assimilate language items after exercise and practice.
(3) Task completion
Students apply the language knowledge that they have learnt to the task they are undertaking. This could also be called language output.
(4) Language consolidation
After practice, students carry out consolidation and enhancement activities by targeting problems that arose in applying the language.
3.Design of Instructional Techniques
Teaching activities cannot happen without the assistance of certain technologies and equipment, ranging from the traditional blackboard to modern facilities such as the internet and multimedia, which could all be advantageous in improving the effectiveness and efficiency of the teaching process. The design of instructional techniques includes the selection and application of instructional media to assist instructional activities. Selection of instructional media and design of activities with media should be aligned with the learning objectives, learning materials, learner characteristics, and instructional strategies.
The functions and characteristics of various instructional media should also be considered. In the instructional process, there is no indispensable media but only effective media and effective use. Selection of instructional media and design of activities using media can have an immediate impact on the achievement of learning objectives and implementation of instructional strategies. In instructional design for English curriculum, it is crucial to select and use suitable audio and video materials and equipment. Instructional media should be selected and used in line with the demands of instructional activities rather than purely for the sake of using something which is modern.
sEvaluation
(1) Identifying Evaluation Standards and Methods for Learning Outcomes
Instructional design is a process to improve the effectiveness of instruction; and the fulfillment of instructional objectives is the key to evaluating the effectiveness of instructional design. Identifying standards for evaluating effectiveness of learning outcomes is a precondition of instructional evaluation. Learning outcome evaluation can take different forms: diagnosis, academic achievement, formative and summative evaluations.
Learning objectives should be taken as the basis for outcome evaluation, while the actual learning condition should be regarded as the criterion for diagnosis evaluation.
Formative evaluation is frequently used in evaluating learning process and its standard can be set according to evaluation needs; while summative evaluation is usually used in academic achievement evaluation and correspondingly its criteria are mainly based on learning objectives.
There are many problems in English instructional evaluation in China. They can be summarized as follows: narrow evaluation criteria, singular means of evaluation, and focus on the study of language items instead of comprehensive language usage.
(2) Formative Evaluation
Formative evaluation refers to finding out how far students are from achieving specified learning outcomes so as to provide them with effective feedback during the instructional process. Both students and teachers engage in the evaluation process which targets improving students' learning behaviors, learning achievements, learning attitudes and emotions as well as strategies during the course of instruction.
Formative evaluation can encourage students to gain a sense of achievement, build stronger confidence, more effectively monitor and readjust their learning process, and thus develop into active, independent learners.
In English curriculum, formative evaluation should be adopted as much as possible to assist teachers in providing precise and timely feedback on student progress and also making adjustments to teaching methods in order to improve the instructional impact.
Formative evaluation in English curriculum should be based on the principle of motivation and recorded in the form of descriptive evaluation, degree ranking or scores. Such scores, however, should not contribute to the final grades.
(3) Summative Evaluation
Summative evaluation is a measurement of student academic performance and achievement at the end of a course of study. Summative evaluation is an important instrument in testing the development of student comprehensive language skills. It should be carried out according to the curriculum standards with an emphasis on an ability to apply English in specific contexts.
The form and content of summative evaluation should comply with the different objectives in various phases of learning.
Based on the general curriculum objectives of comprehensive language skills set in the National Curriculum Standards, the summative examination questions should mainly focus on checking language application in real contexts and strike a balance between the amount of subjective and objective questions.
Feedback and Modification
Feedback and modification refer to the adjustment of instructional design based on feedback from evaluation in order to improve the effectiveness of instruction.
Instructional design should not be considered as fixed and unchangeable but rather as a process under which constant and timely adjustments should be made according to instructional information collected from feedback.
In practice, experienced teachers usually take advantage of feedback to adjust instructional strategies, thereby promoting the effectiveness of instruction.
Instructional design is rational teaching preparation that can improve a teacher's teaching through practice and experience and thereby help inexperienced teachers learn and develop rapidly.
Due to problems and difficulties such as students' lack of skills and knowledge, and poor teaching environment and conditions, English instructional design requires that teaching strategies be modified in a timely manner based on the feedback in the instructional process.
【Practical Analysis】
Analyse the following teaching activities from the perspective of learners: